Understanding how to find formal charge is one of the most important foundational skills in chemistry. Formal charge helps students determine the most stable Lewis structure, predict molecular behavior, and understand why atoms arrange themselves the way they do in molecules. While the calculation itself looks simple, many learners struggle because they don’t fully understand why formal charge matters or how to apply it correctly.
Formal charge is not a real electrical charge—it is a theoretical bookkeeping tool used by chemists to compare possible Lewis structures and identify the most stable arrangement of electrons. From general chemistry exams to advanced molecular modeling, the ability to calculate and interpret formal charge is essential.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to find formal charge in chemistry, including how to calculate it for atoms, elements, Lewis structures, and entire molecules. Each section explains the concept clearly, step by step, using logic, examples, and practical reasoning rather than memorization.
How to Find Formal Charge in Chemistry
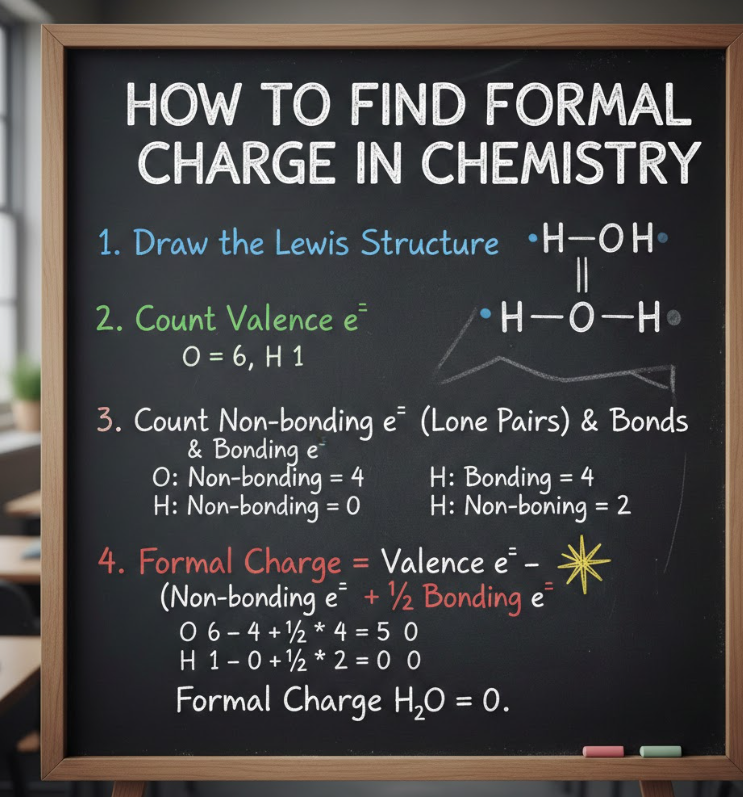
Formal charge is a calculated value that assigns electrons to atoms within a molecule based on ownership rules. It helps chemists evaluate whether electrons are distributed in a chemically reasonable way.
The general formal charge formula is simple, but understanding how each term works is key.
Core Principles of Formal Charge
• Formal charge is a comparison tool, not a real charge
Formal charge does not represent the actual electrical charge of an atom. Instead, it compares how many electrons an atom should have (based on its position in the periodic table) versus how many it is assigned in a Lewis structure.
• Electrons are assigned by simple rules
In formal charge calculations, lone-pair electrons belong entirely to the atom, while bonding electrons are shared equally between bonded atoms, regardless of electronegativity.
• The goal is stability, not zero at all costs
While the most stable structures usually minimize formal charges, sometimes non-zero formal charges are unavoidable. The most reasonable structure distributes charges logically.
• Formal charge helps choose the best Lewis structure
When multiple valid Lewis structures exist, the structure with the lowest total formal charge and minimal charge separation is usually preferred.
• Formal charge relates to reactivity
Atoms with positive formal charge tend to attract electrons, while atoms with negative formal charge often act as electron donors.
• Formal charge supports deeper chemical understanding
Mastering formal charge improves understanding of resonance, molecular geometry, and reaction mechanisms.
Also Read:- How to Cook Plantains: A Complete Guide for Every Cooking Method
How to Find Formal Charge of an Atom
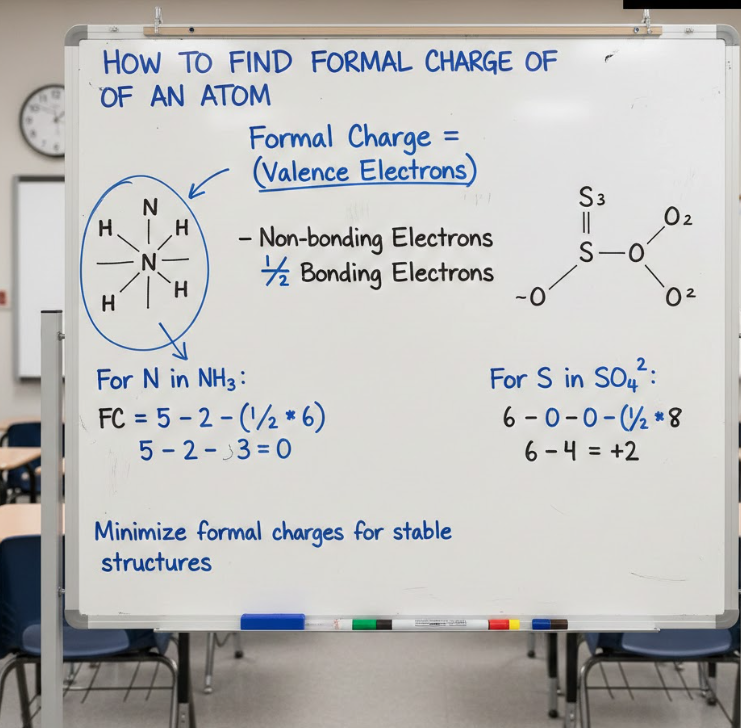
Learning how to find formal charge of an atom requires understanding how electrons are counted and assigned within a molecule. Each atom is evaluated individually, even though it exists within a larger structure.
The calculation uses a consistent, logical process that works for any atom in any molecule.
Step-by-Step Method for an Atom
• Identify valence electrons
Valence electrons are determined by the atom’s group number in the periodic table. For example, carbon has four valence electrons, oxygen has six, and nitrogen has five.
• Count lone-pair electrons
Lone-pair electrons are fully owned by the atom. Every lone pair contributes two electrons toward the atom’s electron count.
• Count bonding electrons carefully
Each bond contains two electrons, but only one electron per bond is assigned to each atom involved.
• Apply the formal charge formula
Formal Charge = Valence electrons − (Lone-pair electrons + ½ Bonding electrons)
• Interpret the result logically
A formal charge of zero indicates balanced electron ownership. Positive values suggest electron deficiency, while negative values suggest excess electrons.
• Check chemical reasonableness
Atoms usually prefer formal charges consistent with electronegativity trends, where more electronegative atoms hold negative charge.
Also Read:- How to Unhide Apps on iPhone: Complete Step-by-Step Guide
How to Find Formal Charge of an Element
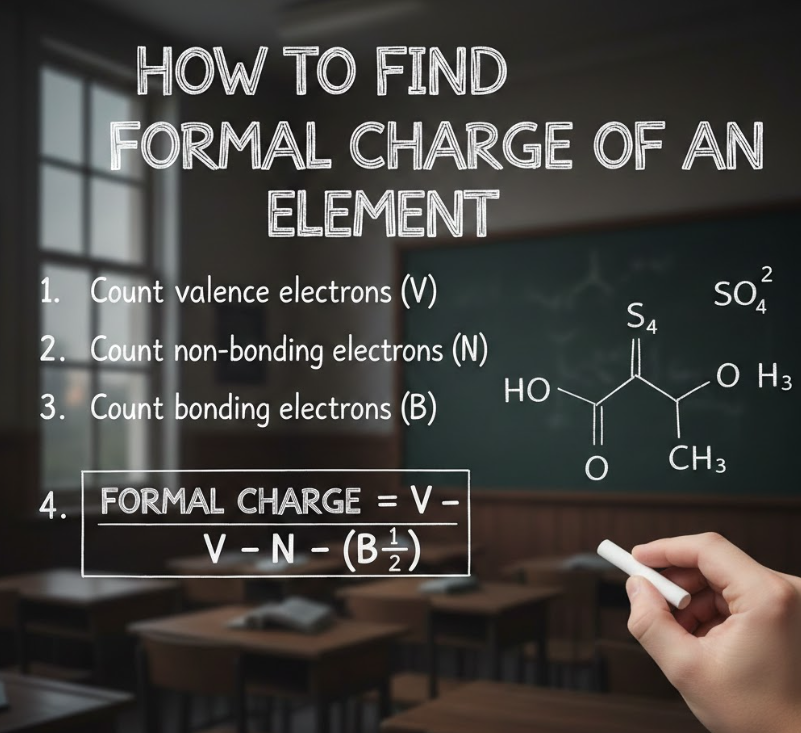
Understanding how to find formal charge of an element builds directly on atomic electron behavior. Elements behave predictably in formal charge calculations based on their periodic trends.
This section focuses on how elements behave consistently across different molecules.
Element-Based Formal Charge Insights
• Group number determines valence electrons
Main-group elements follow predictable valence patterns, making formal charge calculations systematic and reliable.
• Metals usually form positive formal charges
Metals tend to lose electrons and often show positive formal charges in compounds.
• Nonmetals often carry negative formal charges
Highly electronegative elements such as oxygen and chlorine frequently carry negative formal charges.
• Hydrogen follows unique rules
Hydrogen always has one valence electron and can only form one bond, simplifying its formal charge calculations.
• Octet rule influences charge stability
Elements strive for stable electron configurations. Formal charges that violate the octet rule are usually less stable.
• Formal charge explains bonding patterns
Why nitrogen forms three bonds and oxygen forms two becomes clearer through formal charge analysis.
Also Read:- How to Wash a Baseball Cap: Complete Cleaning Guide Without Damage
How to Find Formal Charge of Lewis Structure

Learning how to find formal charge of Lewis structure is where theory becomes practice. Lewis structures visually represent electron distribution, making formal charge calculations straightforward when done correctly.
This process applies to every atom shown in the structure.
Lewis Structure Formal Charge Process
• Draw the correct Lewis structure first
Formal charge calculations only work when the Lewis structure correctly represents all valence electrons.
• Label all lone pairs and bonds clearly
Missing electrons lead to incorrect formal charges. Precision matters.
• Calculate formal charge for each atom individually
Every atom must be evaluated separately using the same formula.
• Compare alternative Lewis structures
Formal charge helps determine which resonance structure is most stable.
• Minimize charge separation
Structures with charges spread far apart are usually less favorable.
• Respect electronegativity trends
Negative formal charges should reside on more electronegative atoms whenever possible.
Also Read:- How to Test a Capacitor: Complete Guide for Accurate and Safe Testing
How to Find Formal Charge of a Molecule
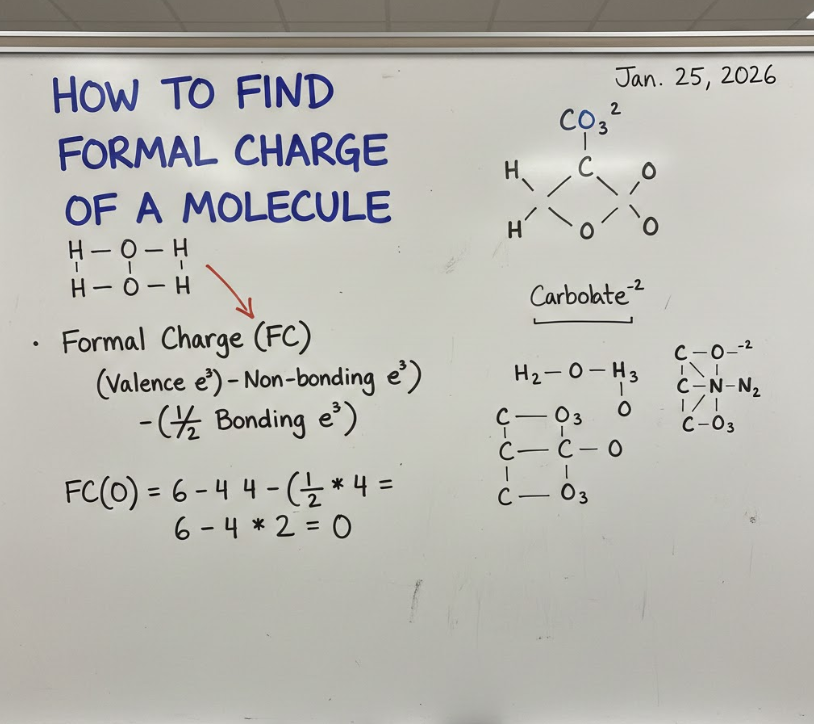
Understanding how to find formal charge of a molecule means evaluating the sum of all atomic formal charges and interpreting the result logically.
This step confirms whether your structure is chemically valid.
Molecular-Level Formal Charge Analysis
• Add all atomic formal charges
The sum of formal charges must equal the overall charge of the molecule or ion.
• Neutral molecules sum to zero
If a molecule is neutral, positive and negative formal charges must balance out.
• Ions reflect net charge correctly
Polyatomic ions show total formal charge equal to their ionic charge.
• Formal charge reveals reactive sites
Regions of negative charge often attract electrophiles, while positive sites attract nucleophiles.
• Helps predict resonance stability
Formal charge comparison identifies dominant resonance contributors.
• Supports molecular geometry understanding
Electron distribution influences shape and bond angles indirectly.
Also Read:- How to Remove Super Glue from Skin: Safe and Effective Methods
How to Find Formal Charge Chemistry (Conceptual Understanding)
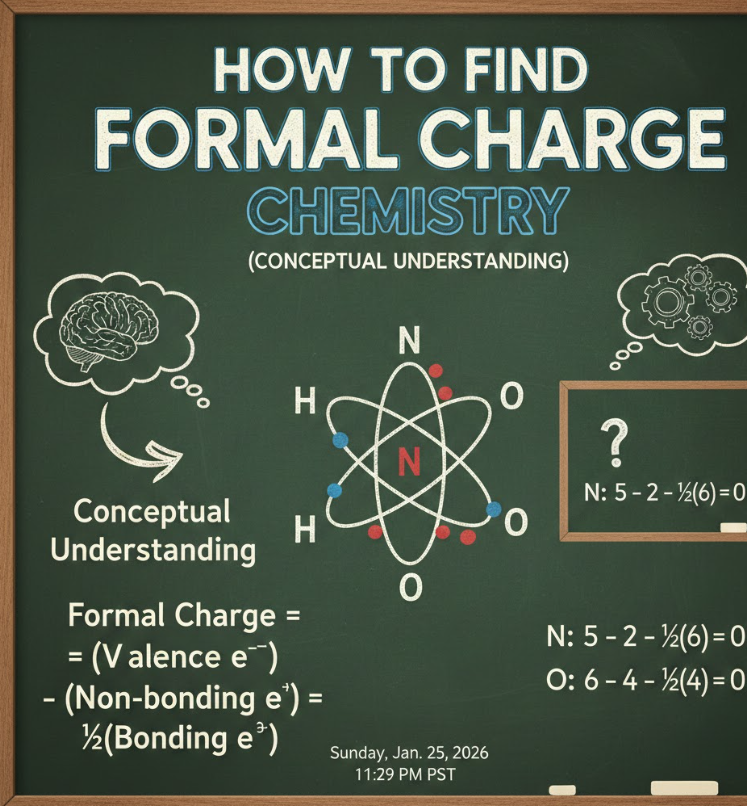
The phrase how to find formal charge chemistry reflects a deeper need to understand why formal charge matters, not just how to calculate it.
This conceptual layer separates memorization from mastery.
Why Formal Charge Matters in Chemistry
• Predicts molecular stability
Lower formal charges usually indicate more stable molecules.
• Explains resonance behavior
Formal charge comparison clarifies why some resonance forms contribute more.
• Connects structure to reactivity
Charge distribution explains reaction pathways and intermediates.
• Supports acid-base reasoning
Atoms with negative formal charge often act as bases.
• Used in advanced chemistry fields
Organic chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science rely heavily on formal charge.
• Builds foundational chemical intuition
Understanding formal charge improves overall chemical reasoning skills.
Also Read:- How to Paint Kitchen Cabinets: A Complete Professional Guide for a Flawless Finish
Conclusion
Learning how to find formal charge is a turning point in chemistry education. It transforms Lewis structures from drawings into meaningful representations of electron behavior. By understanding how to calculate formal charge for atoms, elements, Lewis structures, and entire molecules, students gain powerful insight into molecular stability and chemical logic.
Formal charge is not just a formula—it is a way of thinking about chemistry with clarity, structure, and confidence.
FAQs
Is formal charge the same as oxidation number?
No. Formal charge is theoretical, while oxidation number assumes full electron transfer.
Can atoms have non-zero formal charge in stable molecules?
Yes. Many stable molecules contain formal charges.
Does formal charge affect molecular shape?
Indirectly. Electron distribution influences bonding and geometry.
Why minimize formal charge?
Lower formal charge generally means greater stability
For More Update Visit: VallayTaxNv