Fractions are a fundamental part of mathematics, yet many learners feel confused or overwhelmed when division enters the picture. Understanding how to divide fractions is not just a classroom requirement — it is a life skill used in cooking, construction, budgeting, measurements, and problem-solving. When taught correctly, fraction division becomes logical, predictable, and surprisingly simple.
This comprehensive guide breaks down how to divide fractions step by step, using clear explanations, real-world reasoning, and practical logic. We will cover dividing fractions with whole numbers, different denominators, mixed numbers, and dividing fractions by whole numbers, all in a way that builds confidence and mastery rather than memorization.
Understanding Fraction Division Before You Begin
Before learning how to divide fractions, it is important to understand what division actually means. Division asks how many times one quantity fits into another. When fractions are involved, division tells us how many fractional parts exist within a given value.
Unlike addition or subtraction, fraction division does not require common denominators. Instead, it relies on the concept of reciprocals — flipping the second fraction and multiplying. This method works because division is the inverse of multiplication.
Once learners understand why this rule works, fraction division stops feeling like a trick and starts making sense. Conceptual clarity is the foundation of long-term mathematical success.
How to Divide Fractions With Whole Numbers

Dividing fractions with whole numbers is often the first challenge students face. The key is understanding that whole numbers can always be written as fractions.
• Converting Whole Numbers Into Fractions
Any whole number can be written as a fraction by placing it over 1. This step allows the division process to follow the same rules used for fractions, making the operation consistent and logical.
• Understanding the Reciprocal Concept
Division by a whole number means multiplying by its reciprocal. For example, dividing by 4 is the same as multiplying by 1⁄4. This preserves the mathematical balance of the equation.
• Step-by-Step Logical Flow
Rewrite the whole number as a fraction, flip it, then multiply. Each step follows naturally from the definition of division rather than memorization.
• Visual Interpretation
Dividing a fraction by a whole number means splitting the fraction into equal parts. This visual understanding helps learners grasp the meaning behind the numbers.
• Reducing Final Answers
Always simplify the result. Reduced fractions are easier to understand and reflect proper mathematical form.
• Common Learning Mistakes
Many students forget to convert the whole number or flip the wrong value. Slowing down and checking each step prevents errors.
Also Read:- How to Descale Keurig: The Complete Guide for Better Coffee and Longer Machine Life
How to Divide Fractions With Different Denominators

Dividing fractions with different denominators often worries students, but it is actually easier than adding or subtracting fractions.
• No Need for Common Denominators
Unlike addition, division does not require matching denominators. This surprises many learners but simplifies the process significantly.
• Flipping the Second Fraction
The denominator difference disappears once the second fraction is turned into its reciprocal. This step transforms division into multiplication.
• Why the Rule Works
Multiplying by a reciprocal keeps the mathematical value consistent. It answers the question of how many groups of one fraction fit into another.
• Keeping Numbers Manageable
Simplifying before multiplying prevents large numbers and reduces calculation errors.
• Real-World Meaning
Dividing fractions with different denominators is common in cooking and measurements where units rarely match perfectly.
• Final Simplification Importance
Always reduce the answer. Simplified fractions communicate results clearly and accurately.
Also Read:- How to Bake Salmon: A Complete Guide to Perfect Oven-Baked Salmon
How to Divide Fractions With Mixed Numbers
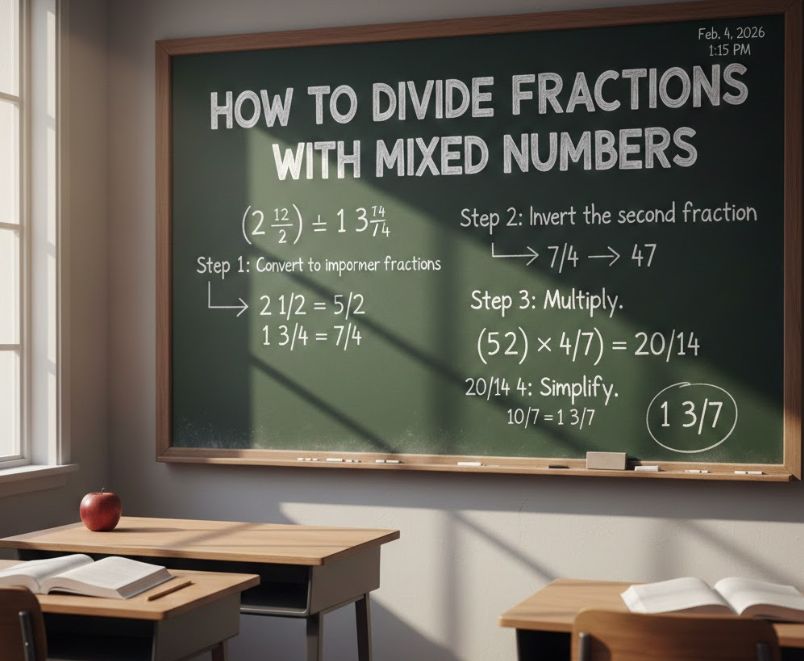
Mixed numbers require an extra step, but once converted properly, the division process is identical to simple fractions.
• Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
Multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place over the original denominator. This conversion is essential.
• Why Conversion Is Necessary
Division rules apply only to fractions, not mixed formats. Improper fractions allow consistent mathematical operations.
• Applying the Reciprocal Rule
After conversion, flip the second fraction and multiply as usual. The structure remains unchanged.
• Managing Larger Numbers
Improper fractions can look intimidating, but simplifying before multiplying keeps calculations manageable.
• Turning Results Back Into Mixed Numbers
Final answers are often converted back into mixed numbers for readability and real-world relevance.
• Avoiding Common Errors
Skipping the conversion step or flipping the wrong fraction leads to incorrect answers. Accuracy depends on process discipline.
Also Read:- How to Lower Body Fat Percentage: A Complete Science-Backed Guide
How to Divide Fractions by Whole Numbers

Dividing fractions by whole numbers is one of the most practical and frequently used fraction skills.
• Understanding Division Direction
Dividing by a whole number asks how many equal parts the fraction can be split into. This helps conceptual understanding.
• Writing the Whole Number as a Fraction
Always convert the whole number to a fraction over 1 before continuing.
• Using the Reciprocal Properly
Flip the whole number fraction, then multiply. This step ensures mathematical correctness.
• Simplification Before Multiplication
Reducing numbers early avoids unnecessary complexity and improves accuracy.
• Real-Life Applications
This method is used in recipes, construction measurements, and time calculations.
• Checking Reasonableness of Results
If dividing by a number greater than 1, the result should be smaller — a helpful way to self-check answers.
Also Read:- How Long Does It Take to Build a House? A Complete Timeline Guide
Why the “Keep, Change, Flip” Rule Works
Many students memorize “keep, change, flip” without understanding it. Understanding the reason makes learning permanent.
• Division is the inverse of multiplication
• Reciprocals preserve numerical balance
• Multiplication answers “how many groups”
• Mathematical consistency across operations
• Conceptual clarity reduces mistakes
• Understanding replaces memorization
Common Fraction Division Mistakes to Avoid
• Flipping the wrong fraction
• Forgetting to convert mixed numbers
• Not simplifying final answers
• Treating division like subtraction
• Rushing through steps
• Ignoring logical result size
Avoiding these mistakes improves confidence and accuracy.
Also Read:- How to Build a PC: The Complete Expert Guide for Beginners and Enthusiasts
Conclusion
Mastering how to divide fractions is a key step toward mathematical confidence and real-world problem solving. Whether you are dividing fractions with whole numbers, mixed numbers, or different denominators, the logic remains consistent and reliable when the correct steps are followed.
By understanding why the process works — not just how — learners build long-term skills instead of temporary memorization. With practice and clarity, fraction division becomes one of the easiest and most useful operations in mathematics.
FAQs
Why do we flip the second fraction?
Because dividing by a number is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
Do fractions need common denominators to divide?
No, only addition and subtraction require that.
Should answers always be simplified?
Yes, simplified answers reflect proper mathematical form.
Is fraction division used in real life?
Yes, in cooking, construction, budgeting, and measurements.
For More Update Visit: VallayTaxNv
